
December 9 2023
8 min read

Aug
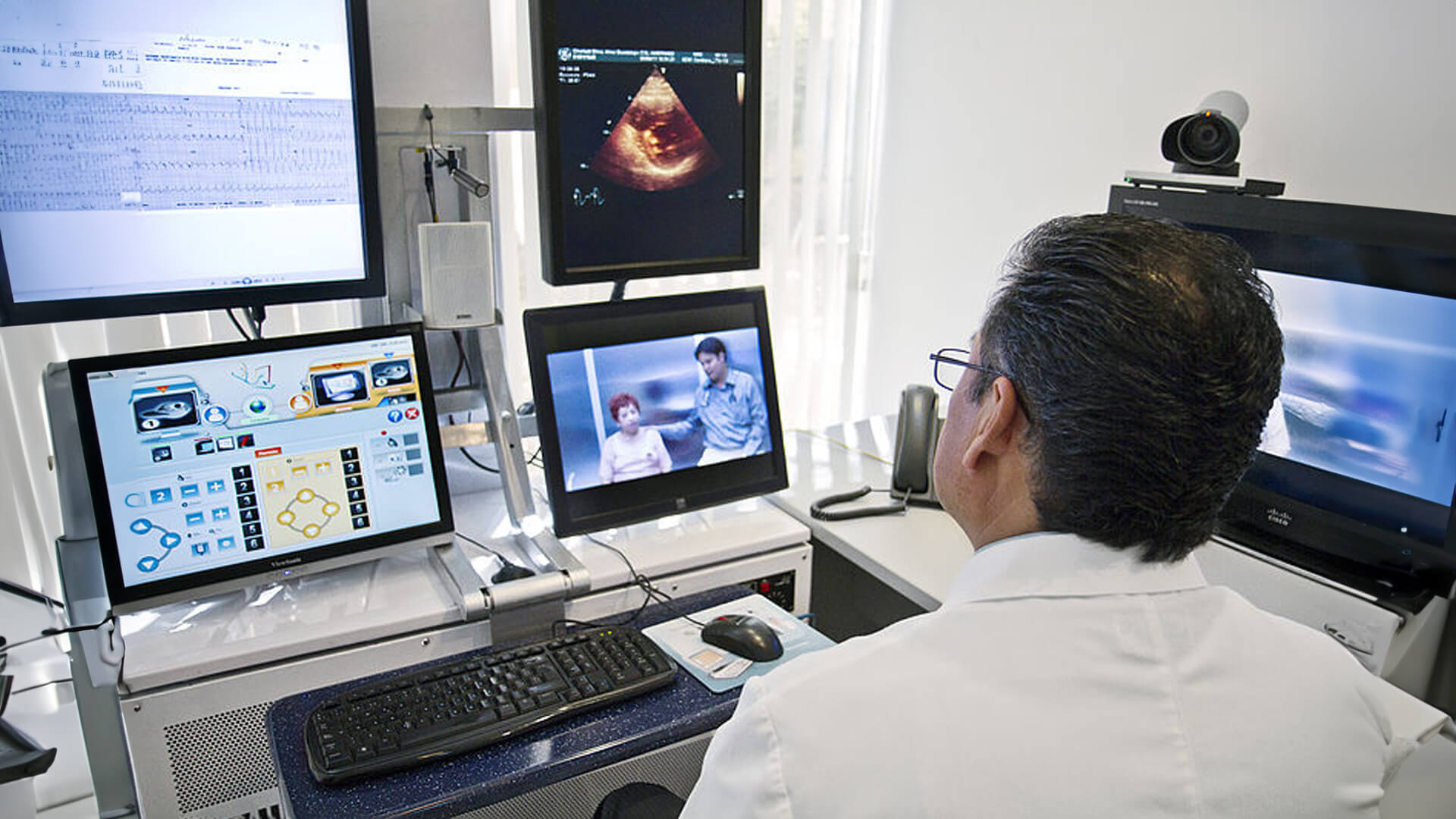
Telemedicine has become an essential part of healthcare, providing remote access to medical care and reducing the need for in-person visits. With the rise of telemedicine, it’s important for healthcare providers to understand the different types available and which one is right for their practice.
In this blog post, we will take a deep dive into the various types of telemedicine and explore their capabilities, features, and applications. From real-time telemedicine to remote patient monitoring, we will cover it all. So, let’s explore the world of telemedicine and find out which type suits your practice best. Let’s get started!
In store-and-forward telemedicine, medical information such as images, videos, or patient records are captured and transmitted to healthcare professionals or specialists for assessment at a later time.
This approach doesn’t require immediate interaction and is especially useful for cases where visual information is crucial, allowing experts to review the data and provide diagnosis or recommendations asynchronously.
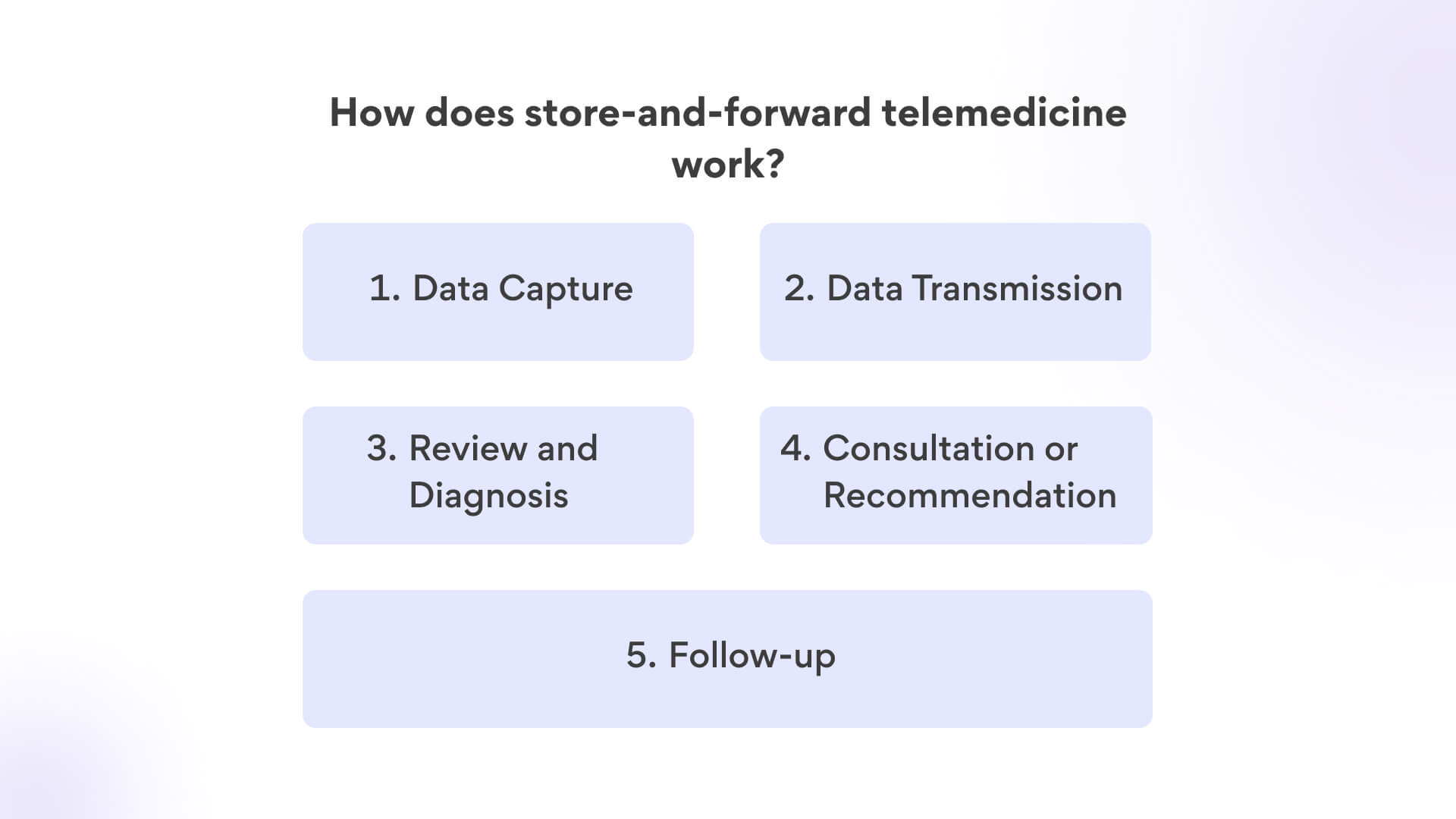
Data Capture: The process begins when a patient or a healthcare provider captures relevant medical information, such as images, videos, or patient history. For instance, a patient might take a photo of a skin rash or a wound.
Data Transmission: The captured data is then transmitted electronically to the healthcare professional or specialist who will review it. This transmission can occur through secure messaging platforms or dedicated telemedicine software.
Review and Diagnosis: The receiving healthcare professional, often a specialist, reviews the transmitted data at a convenient time. This might involve examining the images, studying patient history, and analyzing any relevant context.
Consultation or Recommendation: After reviewing the information, the healthcare provider provides a diagnosis, treatment recommendations, or further instructions. This could be done through secure messaging, email, or a follow-up appointment if needed.
Follow-up: Depending on the outcome, there might be a need for further communication or follow-up. If the condition requires in-person assessment, the patient might be advised to schedule an in-person visit.

This method is commonly used in medical specialties where visual information plays a crucial role:
Dermatology: Dermatologists often use store-and-forward telemedicine to receive images of skin conditions, rashes, or lesions. Patients can take pictures of their skin issues and send them to dermatologists for remote assessment.
Radiology: Radiologists use store-and-forward telemedicine to review medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. These images can be sent electronically to specialists for interpretation and consultation.
According to American Medical Association, Radiologists are the biggest users of telemedicine's data storing-and-forwarding function.
Pathology: Pathologists can receive digital images of tissue samples and slides for analysis. This is particularly useful in cases where physical samples cannot be transported quickly or when a second opinion is needed.
Ophthalmology: Ophthalmologists utilize store-and-forward telemedicine for eye condition assessments. Patients can send images or videos of their eyes for remote consultation on issues such as redness, irritation, or potential retinal problems.
Efficient Specialist Consultations: Store-and-forward telemedicine enables patients to receive expert opinions from specialists regardless of their location. This approach eliminates the need for patients to travel long distances, making it especially useful for cases that require specialized assessment.
Time Flexibility: Patients and healthcare professionals can engage at their convenience. Specialists can review cases during non-peak hours, leading to reduced waiting times for patients and quicker access to medical advice.
Enhanced Documentation: By storing digital records and images, this telemedicine method creates a comprehensive database that facilitates accurate tracking of changes over time. This is particularly beneficial for monitoring the progress of chronic conditions.
Privacy and Comfort: Patients can capture images or videos of sensitive areas in the privacy of their homes, leading to increased comfort and willingness to share potentially embarrassing or personal medical information.
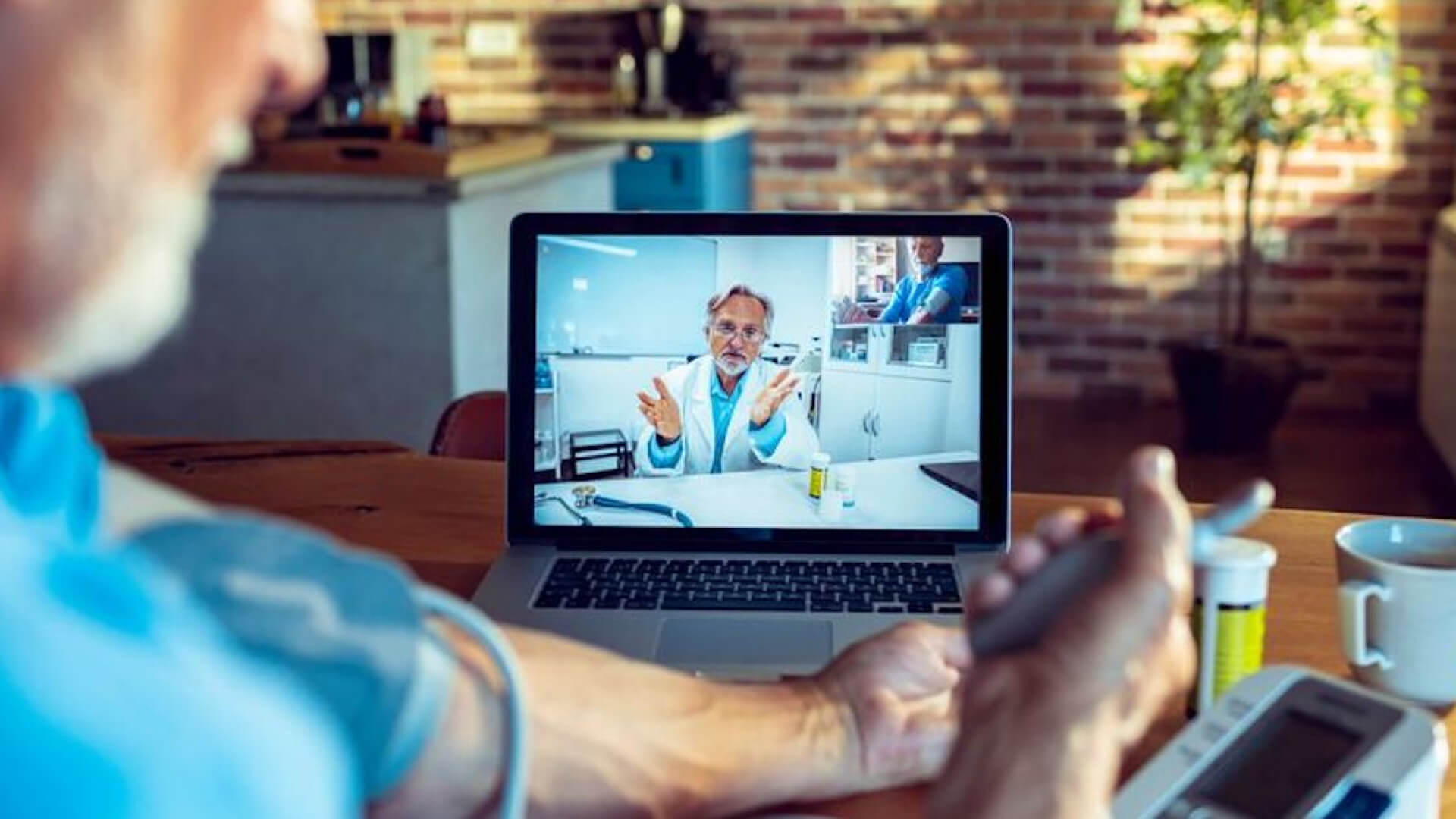

Remote monitoring involves the continuous collection and transmission of patients’ health data using various medical devices such as wearable sensors, glucometers, or blood pressure monitors.
This real-time data is securely sent to healthcare providers who analyze trends and changes, enabling them to manage chronic conditions more effectively and intervene promptly if significant deviations occur.
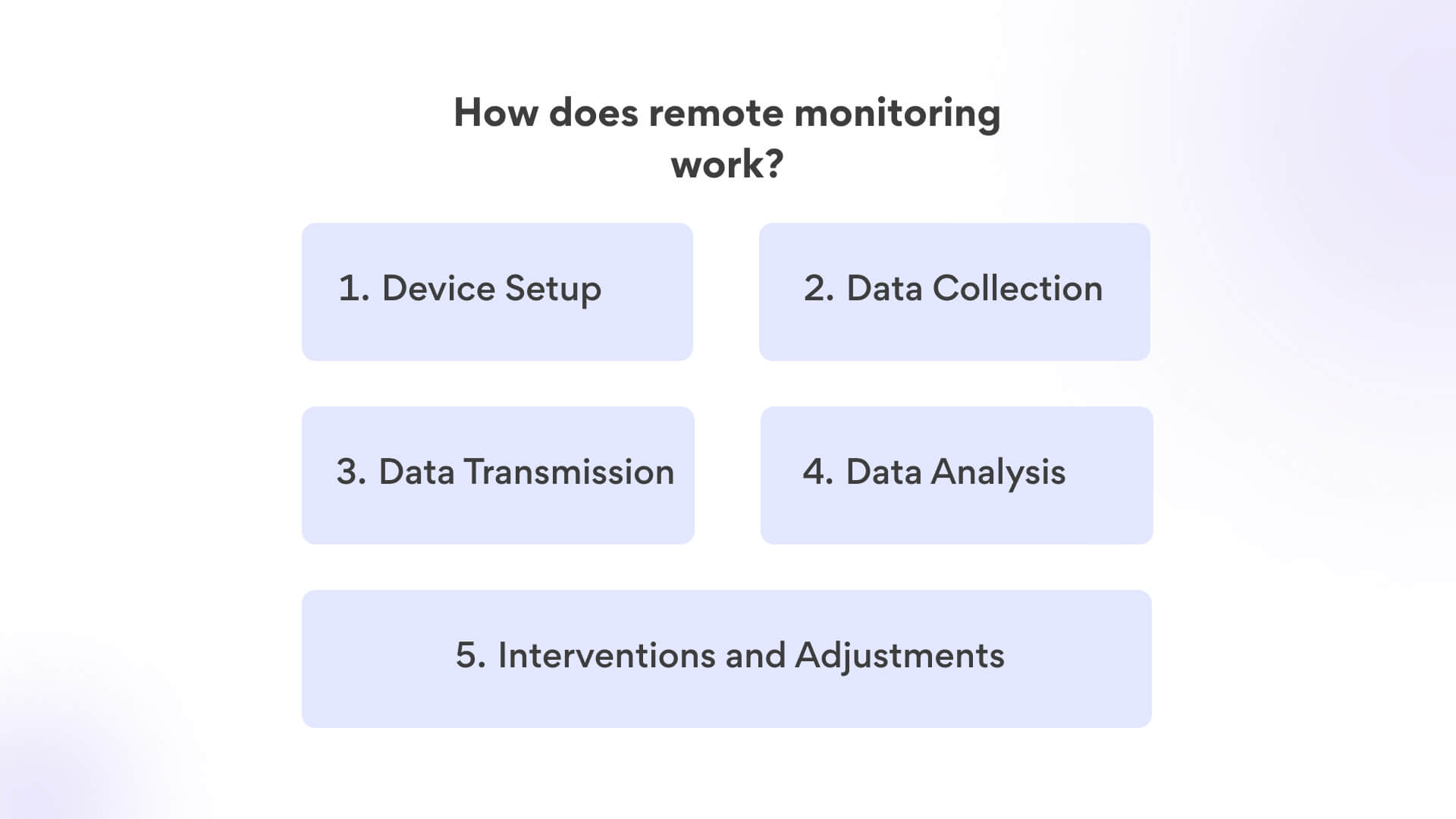
Device Setup: The process starts with the setup of medical devices that can capture and transmit relevant patient data. These devices can include wearable sensors, blood glucose monitors, blood pressure cuffs, and more.
Data Collection: The devices continuously monitor the patient’s health parameters, such as heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, oxygen saturation, or other specific metrics related to the patient’s condition.
Data Transmission: The collected data is sent in real-time or at scheduled intervals to a secure digital platform. This platform can be accessed by healthcare professionals, either directly or through an intermediary system.
Data Analysis: Healthcare providers or specialized monitoring teams review the transmitted data to identify trends, anomalies, or any potential health concerns. They can set up alerts to be notified of critical changes.
Interventions and Adjustments: If any concerning trends or values are detected, healthcare professionals can intervene by reaching out to the patient with guidance, recommendations, or adjustments to treatment plans.
According to Insider Intelligence, 70.6 million US patients, or 26.2% of the population, will use RPM tools by 2025.
This approach is especially beneficial for managing chronic conditions and ensuring timely interventions.
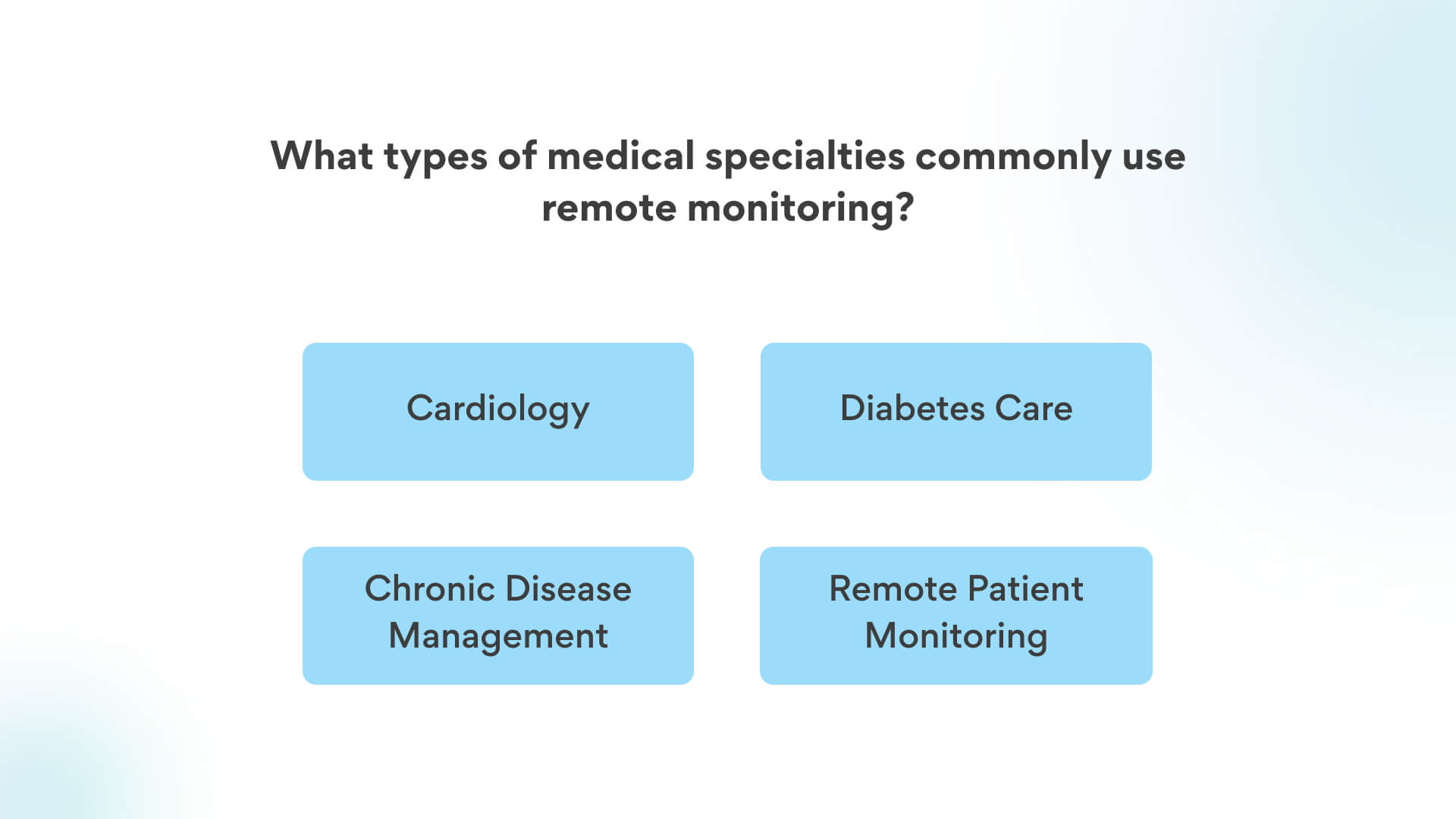
Cardiology: Cardiologists can remotely monitor patients with heart conditions by collecting data from wearable devices, such as heart rate monitors or ECG devices. This helps in managing arrhythmias, heart failure, and post-operative care.
Diabetes Care: Patients with diabetes can use remote monitoring to track their blood glucose levels and share the data with healthcare providers. This enables better management of insulin dosages and overall glycemic control.
Chronic Disease Management: Various chronic conditions, like hypertension and COPD, can be managed through remote monitoring. Patients’ vital signs, such as blood pressure and oxygen saturation, can be continuously tracked, allowing doctors to adjust treatment plans as needed.
Remote Patient Monitoring: This broad application includes monitoring patients after surgeries or during recovery from illnesses. It ensures that patients are healing properly and allows healthcare providers to address any complications early.
Early Intervention: Remote monitoring allows healthcare providers to detect changes or abnormalities in patients’ health data in real time. This enables early intervention, preventing the progression of certain conditions and reducing the risk of complications.
Personalized Treatment Plans: By closely monitoring patients’ vital signs and health trends, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans based on individual responses. This optimization enhances patient outcomes and improves adherence to recommended therapies.
Reduced Hospital Visits: Regular remote monitoring decreases the need for frequent in-person visits, saving both patients and healthcare systems valuable time and resources. Hospitalizations can also be prevented through timely interventions.
Data-Driven Insights: Remote monitoring generates a wealth of data that can be analyzed for patterns and trends. These insights provide a deeper understanding of patient health and aid in refining treatment strategies.
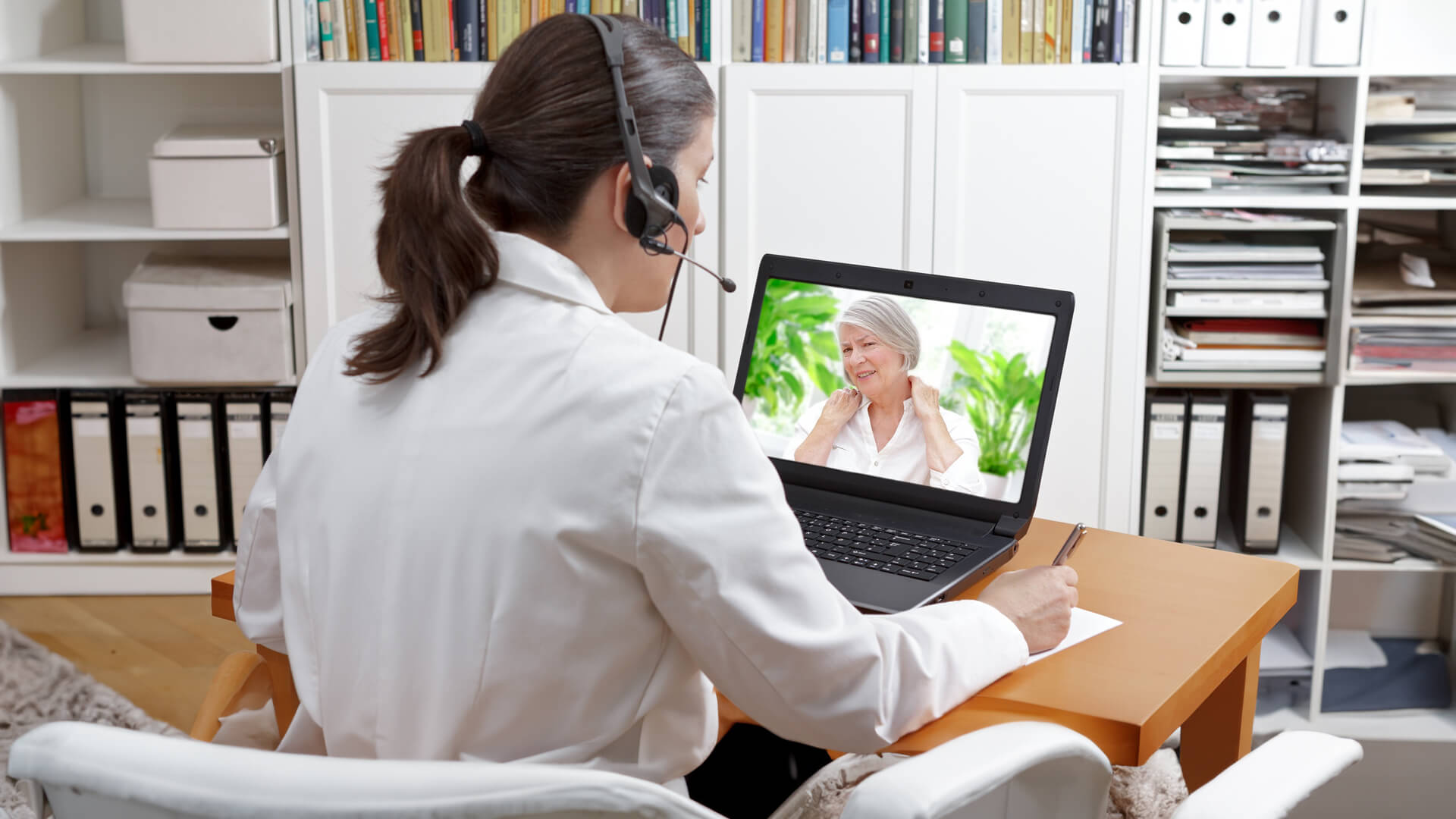

Real-time interactive telemedicine enables patients and healthcare providers to engage in live video or audio consultations, replicating the experience of an in-person visit. This approach allows immediate communication, visual examination, and real-time discussions.
It’s particularly valuable for medical specialties where direct interaction and visual cues are essential, offering patients and providers a way to connect regardless of geographical constraints.
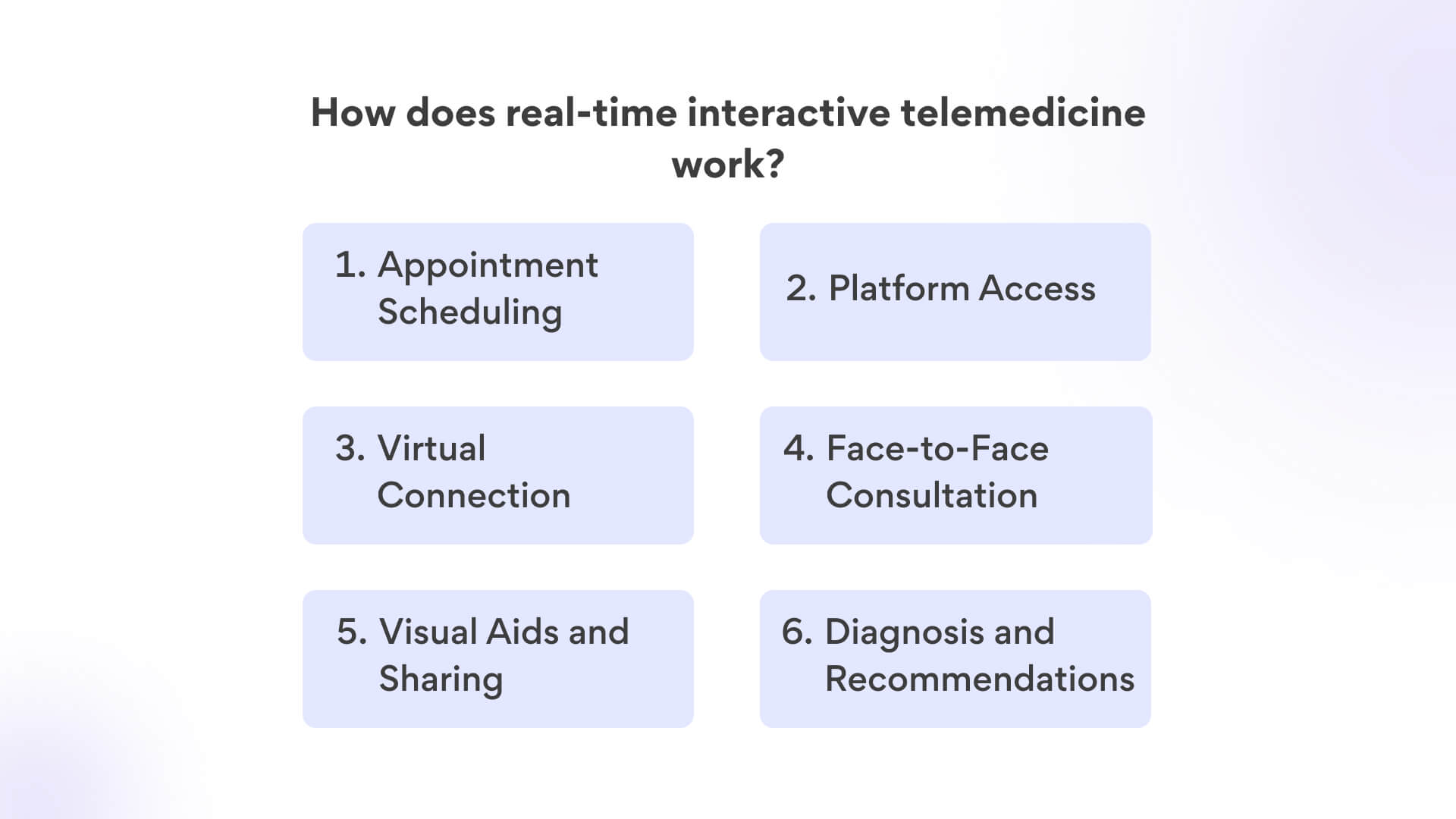
Appointment Scheduling: The process begins with the patient or a healthcare provider scheduling a virtual appointment. This can be done through telemedicine platforms, apps, or online scheduling systems provided by healthcare institutions.
Platform Access: Both the patient and the healthcare provider need access to a secure and HIPAA-compliant telemedicine platform. This platform enables real-time audio and video communication.
Virtual Connection: At the scheduled time, both parties log in to the telemedicine platform. They establish a live video or audio connection, simulating an in-person consultation.
Face-to-Face Consultation: During the virtual appointment, the healthcare provider and the patient engage in a discussion similar to an in-person visit. The provider can ask questions, assess symptoms, and visually examine the patient through video.
Visual Aids and Sharing: The platform often allows the sharing of visual aids such as medical images, test results, or charts. This enhances the communication between the healthcare provider and the patient.
Diagnosis and Recommendations: Based on the conversation, examination, and any shared information, the healthcare provider offers a diagnosis, treatment recommendations, prescriptions, or further tests if necessary.

This approach simulates in-person visits and is particularly suitable for specialties that require immediate interaction.
Psychiatry: Psychiatrists use real-time interactive telemedicine to conduct therapy sessions and assessments. Video calls enable visual cues and real-time discussions, making it effective for managing mental health conditions.
Primary Care: General practitioners can connect with patients virtually to discuss symptoms, provide medical advice, and even prescribe medications when appropriate. This approach enhances accessibility to basic healthcare services.
Neurology: Neurologists can remotely evaluate patients with neurological disorders, such as seizures or headaches. Video consultations allow for observing symptoms and providing timely recommendations.
Internal Medicine: Internal medicine physicians often use real-time telemedicine for general medical consultations, follow-up appointments, and reviewing lab results, all while directly interacting with patients.
Benefits of real-time interactive telemedicine
Immediate Care Access: Real-time interactive telemedicine offers patients swift access to medical advice, especially in urgent situations. This can help alleviate concerns, offer guidance, and prevent unnecessary emergency room visits.
Visual Examinations: Medical professionals can visually assess patients’ conditions, enabling accurate evaluations of symptoms, skin issues, or physical complaints that require direct observation. This feature is particularly valuable in specialties like dermatology.
Personal Connection: Real-time interactions foster a sense of rapport between patients and healthcare providers. Patients feel heard and engaged, which can improve their understanding of medical advice and enhance their commitment to treatment plans.
Convenient Follow-Up: Patients can easily follow up with healthcare providers without the need for travel. This convenience encourages adherence to treatment plans and facilitates ongoing communication for better health management.
It’s clear that no one-size-fits-all solution exists within the realm of telemedicine. Rather, these different types of telemedicine cater to diverse scenarios, each playing a crucial role in delivering accessible, efficient, and patient-centered care.
So whether you’re a healthcare provider striving to elevate patient services or an individual seeking convenience and expertise in one, the path of telemedicine has opened doors to a new era of healthcare possibilities. As technology continues to advance, the journey of telemedicine remains an ongoing narrative, promising improved patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare experiences for all.
Selecting the ideal telemedicine platform
It’s essential to consider another vital aspect of your healthcare journey: selecting the right telemedicine platform. Just as each type of telemedicine offers distinct advantages, a well-suited platform ensures that your healthcare experience is accessible, efficient, and tailored to your needs.
At Confy, we understand the significance of this choice. Our comprehensive white-label platform eliminates technological concerns, allowing you to focus solely on your healthcare journey. Feel free to get in touch with us today, and let’s begin a chat that will shape the way you experience healthcare. Your seamless telemedicine experience starts here.

December 9 2023
8 min read

December 4 2023
8 min read

November 30 2023
8 min read

November 22 2023
8 min read