Telemedicine: a brief overview
In a time when technological advancements in the medical world have progressed to new heights, access to basic medical care is still a tall order for many of those who are economically weak or reside in remote and rural areas. The American entrepreneur and developer of Word Press, Matt Mullenweg said, “technology is best when it brings people together.” Telemedicine can certainly live up to that comment.
Simply put, telemedicine is the use of technology to virtually connect healthcare providers with patients for services like primary diagnosis, healthcare monitoring, discourse, and deliberation, etc.
The past, present, and future of telemedicine as an industry has been and will be guided by the four key stakeholders: Healthcare Providers, Healthcare Receivers, Telemedicine and Peripheral Companies, and last but not the least, the Government.
The US giant, Amazon introduced a digital healthcare program for its employees in 2019. The US Penn State Health also uses telemedicine to monitor nearly a quarter of its ALS patients’ health.
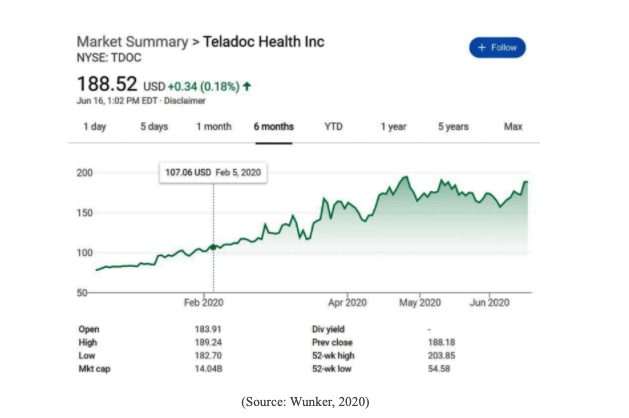
According to the telemedicine Market Share Report- Global 2020-2026 Industry data, the market value of the telemedicine industry is predicted to rise from $45 billion in 2019 to $175 billion in 2026 with a 19.3% CAGR (2020-2026). In May 2020, a CNBC report revealed that telemedicine companies are now climbing the stock market as the global health consumer trends have exponentially shifted towards digital health. The shares of telehealth big-shots like Teladoc have jumped to 48%, One Medical to 52% while American Well and Mindstrong raised $200 million and $100 million capital respectively.
Telemedicine to patients
Over the last decade, healthcare has become increasingly difficult to afford, especially when it comes to treating the most vulnerable, elderly population who comprise more than fifty percent of the global share of healthcare consumers. Besides the issue of lofty expenses, the much older generation and chronically ill patients face difficulty with regular hospital visits. Telemedicine can tackle both the cost and the comfort factors by virtual diagnosis through necessary software, real-time health monitoring using portable hardware and wearable gadgets, thereby eliminating the cost of maintaining spaces, electricity, additional nursing human resources, etc.
Telemedicine to healthcare providers
For the healthcare providers, telemedicine will be a boon in the sense that it will allow them to provide their services to a larger number of patients through an effectively streamlined and highly-regulated system. Constant information sharing and monitoring using technological interfaces will also help them to diagnose chronic cases at an early stage. Besides, telemedicine can use technology to store, update, and retrieve and share a patient’s medical history. This data can tremendously help physicians by saving time before actual diagnosis or treatment or even surgery and can help to solve patient-specific medical puzzles. Another major advantage of telemedicine lies in the area of epidemiological surveillance using technologies like GIS (Geographical Information System)
Role of Governments in shaping the future of Telemedicine
The Covid-19 pandemic has changed many governments’ perspectives on digital healthcare. For something that was grossly neglected even as an alternative, with many countries like the US denying reimbursement or pay-parity, the telemedicine industry is now deemed to be the brand new future of mainstream healthcare. In recent developments, the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced that it will cover telemedicine consultations by physical and occupational therapists aside hospital-based physicians. In March, 2020, the US Federal Government pledged to infuse $29 million to the country’s Telehealth Network Grant Program (TNGP) over a period of five years beginning with 2021 (Weigel et al., 2020). This was done via the CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act. Similarly, a large number of guidelines and regulations have been set up by the Health Council of Italy which has been widely implemented. The Indian government implemented the SAARC e-network telemedicine project to provide digital healthcare to all SAARC nations.
Conclusion
At this nascent stage, telemedicine can have some limitations and face challenges in areas like privacy, accuracy, acceptance from consumers and doctors alike. Yet, with the right amount of regulation and technological manipulation, and innovative breakthroughs, the telemedicine industry can surely become a popular replacement for conventional in-patient primary care. It will not only diffuse boundaries but also promise cheaper and readily accessible healthcare for all.
References
- Drees, J., 2020. 18 Federal Government Updates On Telehealth In Response To COVID-19: The Trump Administration, CMS And Other Federal Agencies Have Issued Several New Policies To Expand The Use Of Telehealth Services During The COVID-19 Pandemic.. [online] Beckershospitalreview.com.
- Mathur, P., Srivastava, S., Lalchandani, A. and Mehta, J.L., 2017. Evolving role of telemedicine in health care delivery in India. Prim Health Care, 7(260), pp.2167-1079.
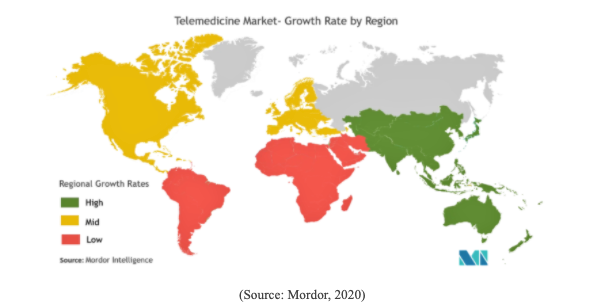
- Mordor, I., 2020. Telemedicine Market | Growth, Trends, And Forecast (2020 - 2025). [online] Mordorintelligence.com.
- Oleg Bestsennyy, e., 2020. Telehealth: A Quarter-Trillion Dollar-Post Covid-19 Reality. [online] mcKinsey.com.
- Schoenberg, R., 2020. Telehealth Momentum Fueling 6 Trends In 2020. [online] Healthcare Analytic News.
- Ugalmugale, S. and Swain, R., 2020. Telemedicine Market Share Report | Global 2020-2026 Industry Data. [online] Global Market Insights, Inc.
- Weigel, G., Ramaswamy, A., Sobel, L., Salganicoff, A., Cubanski, J. and Freed, M., 2020. Opportunities And Barriers For Telemedicine In The U.S. During The COVID-19 Emergency And Beyond. [online] KFF.
- Wunker, S., 2020. How To Make The Coronavirus-Led Growth Of Telehealth Into An Investment Thesis. [online] Forbes.
- Wunker, S., 2020. How To Make The Coronavirus-Led Growth Of Telehealth Into An Investment Thesis. [online] Forbes.